It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family and generally produced due to thermal combustion. Moreover, there are numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is utilized in various industrial processes including synthetic chemical manufacturing and metallurgy, however, it is also a problematic air pollutant arising from industrial activities.
CAS no: 630-08-0
Properties
Generic Properties
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | CO | - |
| Molecular Weight | 28.01 | - |
| Heat of Combustion | 10103.4 | kJ/kg |
| Boiling Point | 81.7 | K |
| Freezing Point | 68.15 | K |
Critical Properties
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Critical Temperature | 132.92 | K |
| Critical Pressure | 34.99 | bar |
| Critical Volume | 93.1 | cm3/mol |
| Critical Density | 0.3009 | g/cm3 |
| Critical Z | 0.295 | - |
| Accentric Factor | 0.066 | - |
Temperature Dependent Properties
Specific Heat
The specific heat at constant pressure can be calculated with the formula:
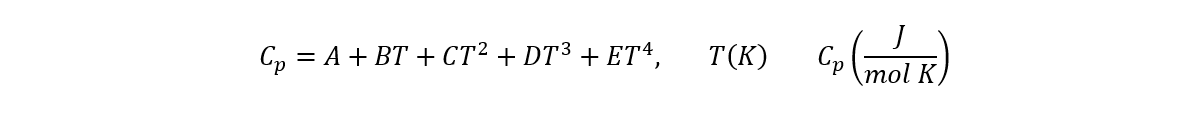
| Constant | Gas | Liquid | Solid |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 29.556 | -19.312 | -6.144 |
| B | -0.0065807 | 2.5072 | 0.95427 |
| C | 0.00002013 | -0.02897 | 0.0021432 |
| D | -1.223E-08 | 0.00012745 | - |
| E | 2.2617E-12 | - | - |
| T min(K) | 60 | 69 | 8 |
| T max(K) | 1500 | 120 | 62 |
Heat of Formation
The heat of formation can be calculated with the formula:
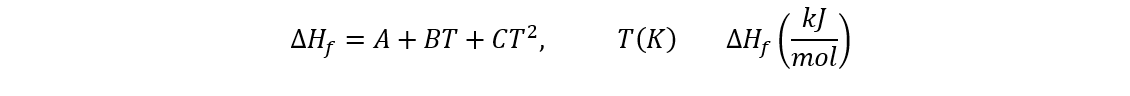
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | -112.56 |
| B | 0.0092553 |
| C | -7.8431E-06 |
| T min(K) | 298.15 |
| T max (K) | 1000 |
Viscosity
The viscosity can be calculated with the formula:
For liquid
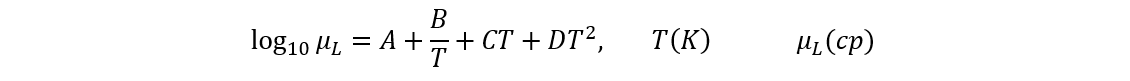
For Gas
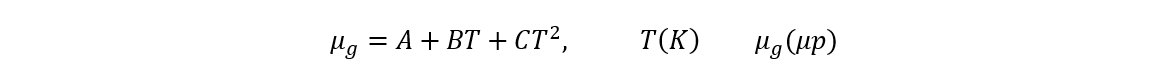
| Constant | Gas | Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| A | 23.811 | -1.1224 |
| B | 0.5394 | 57.858 |
| C | -0.00015411 | -0.0049 |
| D | - | 8.2233E-06 |
| T min(K) | 68 | 69 |
| T max(K) | 1250 | 133 |
Heat of Vaporization
The heat of vaporization can be calculated with the formula:
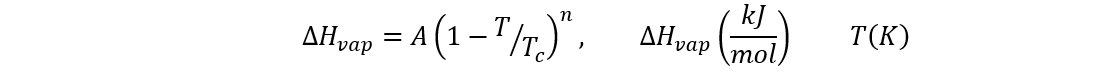
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | 8.003 |
| n | 0.318 |
| T min(K) | 68.15 |
| T max(K) | 132.92 |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity can be calculated with the formula:
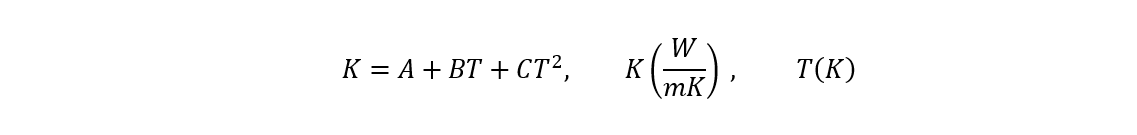
| Constant | Gas | Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.00158 | 0.2269 |
| B | 0.000082511 | -0.00046431 |
| C | -1.9081E-08 | -6.8418E-06 |
| T min(K) | 70 | 68 |
| T max(K) | 1250 | 126 |
Liquid Density
The Liquid Density can be calculated with the Equation:
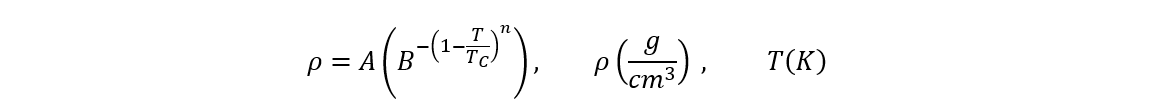
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | 0.2982 |
| B | 0.2766 |
| n | 0.2905 |
| T min(K) | 68.15 |
| T max(K) | 132.92 |
Saturation Pressure
The Saturation Pressure can be calculated with the Antoine Equation:
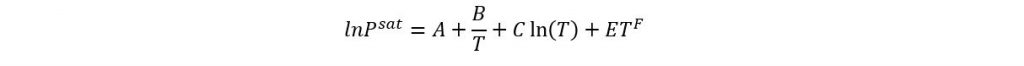
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | 45.698 |
| B | -1076.6 |
| C | -4.8814 |
| E | 7.5673E-5 |
| F | 2 |
| T min(C) | |
| T max(C) |
Diffusion Coefficient at Infinite Dilution in Water
The Diffusion Coefficient at Infinite Dilution in Water can be calculation:
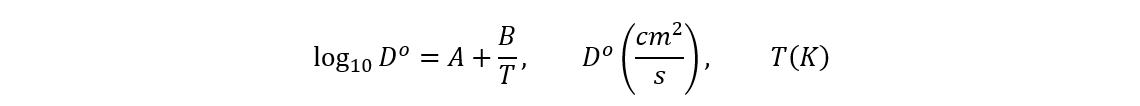
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | -1.2761 |
| B | -1030.203 |
| T min(K) | 274 |
| T max(K) | 394 |
Diffusion Coefficient in Air
The Diffusion Coefficient in Air can be calculated with the Equation:
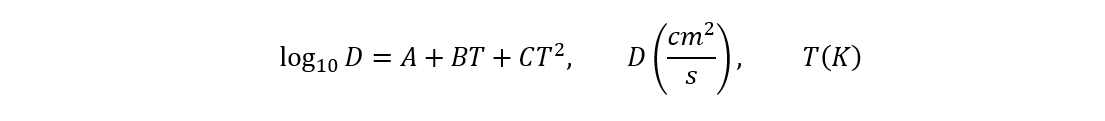
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| A | -0.09388 |
| B | 0.00063041 |
| C | 1.1015E-06 |
| T min(K) | 200 |
| T max(K) | 1000 |